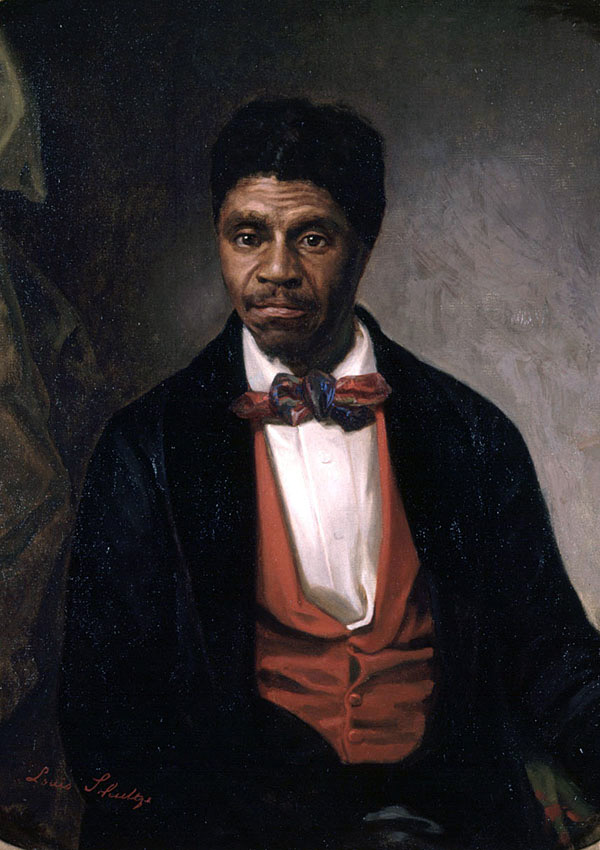Hillary Clinton is in the news this weekend over comments she made regarding the rights of unborn persons, or, more to the point, that in her mind the unborn person does not have constitutional rights (video here).
The exact phrase is, “the unborn person doesn’t have constitutional rights.” What makes this much worse than her usual pro-abortion position is that she admits that the unborn are persons. This means that there are persons who may or may not have constitutional rights, depending upon legislation or court decisions.
This may be a slip of the tongue, betraying a belief she really shouldn’t want the public to know. In law, everyone from birth to the grave are called “persons.” She has, identified the unborn as person, but a person who has no constitutional protection. Let that soak in a minute. There is, in her thinking, a group or class of persons who do not enjoy the protection of law.
The next questions must be, “Why only that particular class of person not protected by the Constitution? Why not the disabled, the very ill, infirm, elderly, or mentally ill?” Can not this class be expanded to include “persons” who are not good fits in society, or those who are too costly look after?
The argument has changed significantly–the pro-life people have always argued that the unborn are persons, and should be treated as such under the law. The pro-abortion people have resisted that terminology, because they know that to do so is to admit that some persons have no protection, and even the most ardent pro-choice advocates weren’t ready for that.
But this weekend, their champion has taken them to this new low point, dividing all human beings into two classes: those with rights and protections, and those without. They leave the distinction to human courts and politicians.
Dred Scott
The infamous Dred Scott Decision of the 1857 US Supreme Court determined that a slave, taken by his master to a state (Illinois) where slavery was illegal, was still not free. This decision, reversed by the Civil Rights Act of 1866 and the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, determined that as a slave, Dred Scott was chattel, or property, of his master. As such, he had no constitutional protection as a citizen, nor was he a person under the law. He had no Constitutional protection.
The Roe vs. Wade decision of 1973 has been likened to the Dred Scott case. After Roe vs. Wade, unborn children are not persons under the law, or protected as persons under the law. Francis Schaeffer addressed this problem in his How Should We Then Live? (quoting Joseph P. Witherspoon, 1916-1995, Jurisprudence Professor at Texas University School of Law):
Thus, the failure of the Court in Roe v. Wade [the abortion case] to have examined into the actual purpose and intent of the legislature in framing the fourteenth amendment and the thirteenth amendment to which it was so closely related and supplementary thereof when it was considering the meaning to be assigned to the concept of “person” was a failure to be faithful to the law or to respect the legislature which framed it. Careful research of the history of these two amendments will demonstrate to any impartial investigator that there is overwhelming evidence supporting the proposition that the principal, actual purpose of their framers was to prevent any court, and especially the Supreme Court of the United States, because of its earlier performance in the Dred Scott case, or any other institution of government, whether legislative or executive, from ever again defining the concept of person so as to exclude any class of human beings from the protection of the Constitution and the safeguards it established for the fundamental rights of human beings, including slaves, peons, Indians, aliens, women, the poor, the aged, criminals, the mentally ill or retarded, and children, including the unborn from the time of their conception.
Francis A. Schaeffer, The Complete Works of Francis A. Schaeffer: A Christian Worldview, vol. 5 (Westchester, IL: Crossway Books, 1982), 222.
Clinton’s position is that unborn children are indeed persons, but some persons remain unprotected under the law. Where Witherspoon worried that the Supreme Court’s decision of 1973 might open the door for others be deemed “non-persons” (“slaves, peons, Indians, aliens, women, the poor, the aged, criminals, the mentally ill or retarded”), Clinton has determined that personhood makes no difference. Personhood does not intrinsically bestow legal protection upon anyone.
Since the US Constitution uses the term “person” (58 times), to include those it protects, it makes sense that if a court deemed someone a non-person (Dred Scott), the protections do not apply.
What Clinton does in this statement is to suggest, unequivocally, no person or class of person is protected by the constitution as an intrinsic right. Protection is bestowed upon, or removed from, a person or persons by legislation or court order.
This is a sure and certain path to tyranny: your rights are for others to determine.